Blockchain, IoT, 5G, cloud computing, augmented reality – these terms are already familiar to many. But what exactly is behind it and why is the business world constantly talking about it? New technologies and digitization are already encroaching on all areas of private and economic life. Special attention is being paid to the globally increasing use of mobile devices and related technology. To stay ahead of the competition, companies must adapt to new ways of working and communicating.
Studies on IT trends are already well elaborated by Gartner. We summarize the 8 megatrends of the future. (part 1)
1. Cloud Computing, Distributed Cloud, Cloud Native
Enterprise data is increasingly migrating to the cloud – and this trend is growing rapidly. Cloud computing is the on-demand provision of IT resources via the Internet at usage-based prices (see Amazon AWS). Companies can access computing power, storage or databases through cloud providers such as Microsoft Azure or Amazon Web Services (AWS) instead of having physical data centers and servers on premises. Many people are already familiar with this from the private sector: e.g. Apple’s iCloud or Google Drive. What exactly is happening here? Documents, photos, videos or contacts are not stored centrally on the iPhone or Android device, but are located on servers at the providers. Among the advantages in the private sphere is, above all, independent access from anywhere. If I want to view the photos I’ve taken, I can do so across multiple devices as long as I log in with my account.
Regardless of type, size or industry, more and more companies are using the cloud for various use cases. These include, for example, data backups, e-mails, virtual desktops or web applications such as Office 365. In business, resources can thus be called up flexibly and variably according to the individual needs of a company. But why do more and more companies use such services and run the risk of outsourcing critical company data? On the one hand, more and more providers (e.g. Microsoft with Office 365 or Adobe) are converting their business model to pay-as-you-go models. This almost forces you to keep up. On the other hand, such cloud models also offer many advantages: Companies can sustainably reduce their IT costs and always have the latest technologies in-house – without having to invest in special hardware.. Cloud computing can be divided into many other subcategories. One of them is WaaS: Workplace as a Service. As an example, we take our own Workplace as a Service model of the company CosH: Via a “cloud platform”, complete IT workstations can be configured as required and rented in a pay-as-you-go model at fixed monthly costs.
2. Blockchain technology

In the news you read more and more about cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum & Co. However, very few people know that the technology behind Bitcoin is the so-called blockchain. But what do real business models based on blockchain look like and how “revolutionary” is it?
Excursus Definition: Simply put, a blockchain is a large, transparent and tamper-proof data set stored on thousands of computers worldwide. The decisive factor here is that all data records in the blockchain no longer have to be verified by a central authority (e.g., a house bank), but are subject to a decentralized control mechanism in that all participants confirm the correctness of the data and events.The blockchain, however, is much more than just the technology behind the cryptocurrency Bitcoin. According to the World Economic Forum (WEF), blockchain technology is an authoritative solution to drive the global economy forward by eliminating various inefficiencies and lack of transparency in global supply chains.
One example: supply chains: In the food industry, the origin of goods is hardly traceable. There are often references to countries or regions of origin on the packaging – but is it possible to verify this? In our opinion, very heavy. Perishable food can be tracked seamlessly from the farm to the moment the consumer takes it off the shelf in the supermarket.At the moment, technology in Germany is still often lumped into the nerdy IT corner or abstract world of finance. While many uncertainties, volatilities (in finance), and technical challenges remain, societal and organizational awareness continues to grow globally.
3. Internet of Things (IoT)
With the Internet of Things (IOT), objects are given an identity and can communicate with each other. Sounds futuristic? Actually, it’s not that far away anymore. There are already, for example, small household helpers (smart home) that can perform tasks without outside intervention. The best known here are, for example, vacuum cleaner robots that can automate applications through the IoT.
A general definition for IoT does not yet exist in the literature. In general, the term is used for the networking of everyday objects or machines in an industrial environment via the Internet. Here, the main focus is on connecting machines and systems in such a way that entire industrial processes can be automated. IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things) is a component of so-called Industry 4.0. The technical basis is the Internet and microprocessor technology.
Many subject areas and megatrends are strongly interconnected. IoT would not even be possible without cloud computing (paragraph 1), 5G (In the next newsletter part 2) or artificial intelligence (paragraph 4). The diversity of IoT technologies results in a wide range of application areas. As with all innovations and revolutions, the Internet of Things not only expands business areas, but also creates entirely new ones along the way. One of the areas where IoT technologies are already often applied in practice is logistics. Supply chains and logistics processes are becoming easier and more efficient thanks to IoT. Thanks to GPS tracking, fleet managers can track when deliveries arrive and coordinate them in a targeted manner. Research into autonomous driving of cars is already being carried out at full speed. Industry giants such as Tesla and Daimler are already installing “autopilots” in their vehicles, networking one car with another.
4. artificial intelligence (AI)
Whether AI can be called the megatrend of the future is questionable. Because artificial intelligence has long since arrived in our everyday lives. Often without us even noticing. Voice assistants in the living room, search engines on the laptop or driving assistance in the car – all these technologies are based on artificial intelligence. Some are critical of such applications and fear the loss of jobs or that intelligent machines will make humans superfluous or even threaten them in the future. On the other hand, AI offers great opportunities for business and society.
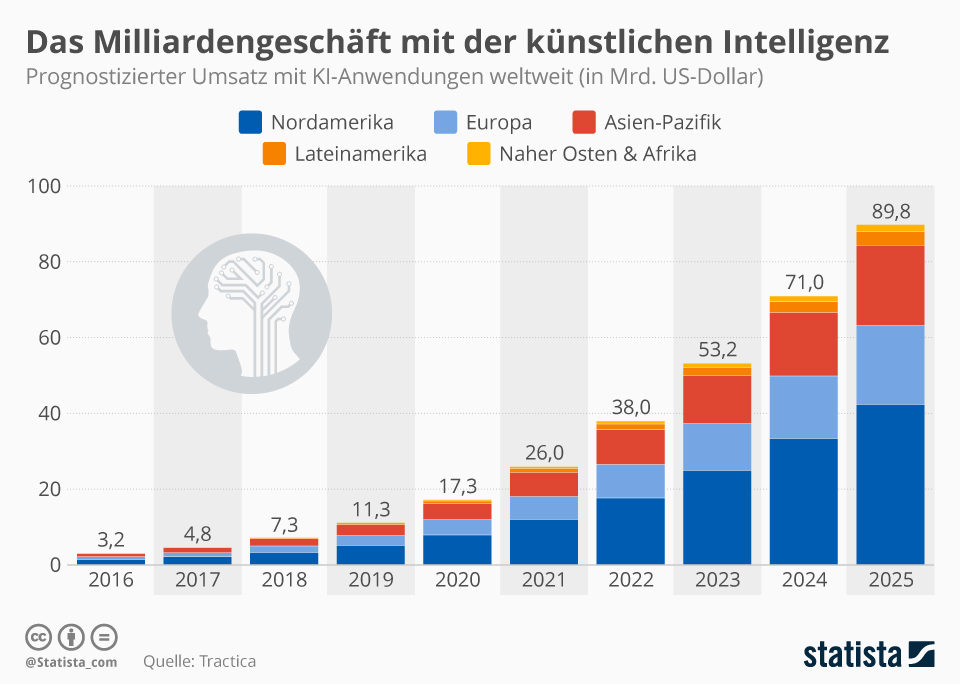
Thus, it can be seen that for the first time in human history, the relationship between humans and machines is changing and self-learning systems are making decisions independently of humans. Meanwhile, more Germans in society see AI as an opportunity. 62% of Germans have a positive attitude toward the topic and only 35% see AI as a threat to society. In 2017, the figures were 48% and 47%, respectively.(Source).
Read our summary of neurotechnology, 5G, 4D printing and augmented reality in our second part of Megatrends.


